Cause of Kidney Failure, Nutrition for Kidney Disease
Table of Contents
One in 10 Malaysians faces kidney problems. Most cases arise due to the food that we eat. So how exactly should we eat to protect our precious kidneys?
Introduction:
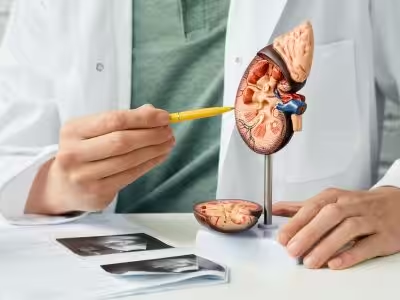
The kidney is an important organ of the human body. The human body has two kidneys where the right kidney is slightly lower because of the liver. Its function is to filter metabolic waste products (such as urea) from the blood and excrete them out of the body through our urine. The kidney has three layers, which contain the nephron and the renal tubules, which make up the renal function system, where certain chemical molecules (such as glucose, amino acids, scales, water, etc) will be recycled. On average, the human body needs to filter 1 litre of blood every hour.
The relationship between kidneys and blood pressure is closely related. Arteriosclerosis caused by an increase in blood lipid leads to an increase in blood pressure, which will damage kidney cells in a long-term high-pressure state. The kidneys also have the function of regulating blood pressure. The kidneys also secrete hormones, such as calcitriol, a special hormone that increases calcium absorption and reabsorption of kidney squamous cells. In addition, the kidneys also secrete Rennin, which functions to control Angiotensin (a hormone that controls vasoconstriction and thereby controls blood pressure) and aldosterone (a hormone that controls the potassium and sodium balance of blood pressure).
How is Kidney Function Calculated?
Generally, we use glomerular filtration rate (GFR) to calculate kidney function. Normal kidney function is above 90, which means that the kidneys can filter 90ml of blood per minute. Kidney failure is not necessarily chronic; acute kidney failure can also occur due to drugs, genes, and other causes. In Malaysia, supplements of unknown origin may be one of the causes of acute renal failure.
It is crucial for the kidneys to control proteinuria (protein in the urine), and haematuria (blood in the urine). Under normal circumstances, there is no protein or blood in urine. But in the case of kidney injury, they are likely to get through the kidney’s filter and flow into the urine.
The following two units are common indicators for understanding kidney index. They are often assessed along with GFR to determine kidney function.
Protein: Creatinine Ratio (PCR): less than15 mg/mmol
Albumin: Creatinine Ratio (ACR): less than3.5, less than 2.5mg/mmol (for male)
If your GFR is 90 and above, you should consume more water, eat more fruits and vegetables and maintain your body weight, blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol at an ideal level. Avoid drinking and smoking. As not everyone can afford dialysis, the best way we can do this is to maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent kidney failure.
We have been talking about some prevention methods, how about those who already had kidney failure, what are the ways to protect our kidneys? (For those with kidney failure stage 3 and above)
If you have diabetes, high blood pressure or have family history, often feel fatigued and have a loss of appetite, it is advisable for you to conduct kidney function test at least once a year, especially if you are 65 and above. If your GFR reading is abnormal, your doctor will confirm with you if you have proteinuria or haematuria. Sometimes checking your PCR is necessary.
Here are Some Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications to Prevent Kidney Failure for Kidney Failure Patients:

- It is not necessary to blindly follow your doctor’s order to stop some of your medications. There is still insufficient evidence that says medication will worsen your condition. As a patient, learn your rights and ask your doctor why before stopping certain medications.
- High blood pressure may worsen kidney failure condition. Hence maintaining your blood pressure at around 130/80 will have a beneficial effect towards your kidney health.
- Control your blood sugar level.
- Maintain your protein intake at 0.6-0.8/kg
- Maintain your proteinuria at less than 1g/day. Evidence shows that for different proteinuria levels at 1g, 2-4g and more than 8g, the probability of the deterioration of kidneys in the next three years is 7.7%, 22.9% and 64.9% respectively.
- Generally, people with kidney problems need to control their potassium intake to 2000-3000mg/day. Foods high in potassium include cocoa-containing foods, bananas, beans, spinach, coconut water, durian and stink beans. To reduce potassium levels in vegetables, you can cut them into small pieces and soak them in warm water. Some spices contain large amounts of potassium, so it is recommended to use spices that have not blended into powder.
- Phosphate is an important nutrient. It is one of the synthesis factors of ATP (energy in the human body), cell membranes, bones, teeth, and genes. However, if your kidneys are not functioning well, controlling your phosphorus intake is necessary. Generally, we recommend controlling phosphorus intake to 800-1000mg/day. Dairy products and meat generally contain high amounts of phosphorus, so their intake must be controlled. Other foods high in phosphorus include canned foods, processed foods and chocolate.
- Limit your salt intake to less than 2400mg a day (approximately 1 teaspoon of salt)
- Although many don’t like to exercise, research shows that controlling your body weight and maintaining BMI in a healthy range may help in delaying kidney failure.
What are Kidney Stones?
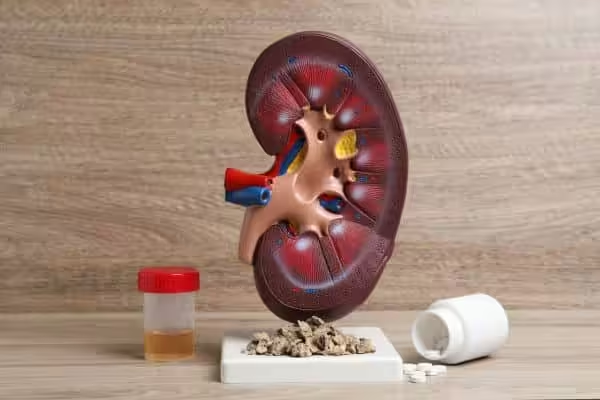
When we don’t drink enough water, the waste inside our body accumulates and crystallizes to form stones. Most stones can be expelled. However, when the stone is too large, surgery may be needed. To reduce the likelihood of kidney stones we must:
- Drink enough water.
- Eat less meat and include more plant protein.
- Obtain vitamins and minerals naturally from vegetables and fruits and avoid relying on health supplements for nutrient.
- Reduce salt intake.
Kidney stones will also increase the risk of kidney failure. To summarise, you will find that in order to protect our kidneys, we have to consume a balanced diet, with 3-4 servings of vegetables and at least 2 servings of fruits every day. Although it sounds cliche, however, if you practice it in long-term, you can definitely see fruitful results if you persist.
As an alternative to extreme diets, Lau recommends the Mediterranean diet. This diet encourages the consumption of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, olive oil, fish, beans and moderate amounts of wine. It is associated with improved heart health and has a better track record of being sustainable and safe in the long run. Additionally, it places importance on lifestyle factors like exercise, sleep, and family meals.
In conclusion, there is no one-size-fits-all diet. The effectiveness and safety of a diet depend on individual needs and circumstances. A balanced diet that considers personal preferences and dietary restrictions is often a more sustainable approach to maintaining health than strict, extreme diets. Consulting a dietitian or nutritionist for guidance is recommended before making significant dietary changes.




